- First Description
- Who gets Buerger’s Disease (the “typical” patients)?
- Classic symptoms of Buerger’s Disease
- What causes Buerger’s Disease?
- How is Buerger’s Disease diagnosed?
- Treatment and Course of Buerger’s Disease
First Description
This disease was first reported by Buerger in 1908, who described a disease in which the characteristic pathologic findings — acute inflammation and thrombosis (clotting) of arteries and veins — affected the hands and feet. Another name for Buerger’s Disease is thromboangiitis obliterans.
Who gets Buerger’s Disease (the “typical” patient)?
The classic Buerger’s Disease patient is a young male (e.g., 20–40 years old) who is a heavy cigarette smoker. More recently, however, a higher percentage of women and people over the age of 50 have been recognized to have this disease. Buerger’s disease is most common in the Orient, Southeast Asia, India and the Middle East, but appears to be rare among African–Americans.
Classic symptoms and signs of Buerger’s Disease
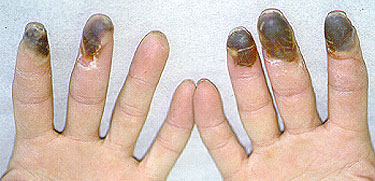
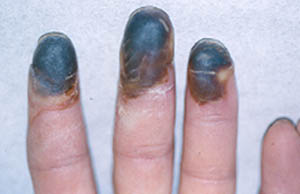
The initial symptoms of Buerger’s Disease often include claudication (pain induced by insufficient blood flow during exercise) in the feet and/or hands, or pain in these areas at rest. The pain typically begins in the extremities but may radiate to other (more central) parts of the body. Other signs and symptoms of this disease may include numbness and/or tingling in the limbs and Raynaud’s phenomenon (a condition in which the distal extremities — fingers, toes, hands, feet — turn white upon exposure to cold). Skin ulcerations and gangrene (pictured below) of the digits (fingers and toes) are common in Buerger’s disease. Pain may be very intense in the affected regions.
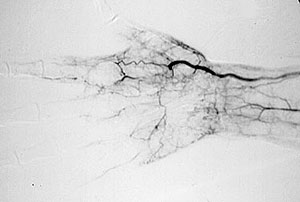
An angiogram demonstrating lack of blood flow to vessels of the hand (figure below). This decreased blood flow (“ischemia”) led to ulcers of the fingers and severe pain.
An abnormal result from an angiogram of the hand (figure below).
Despite the severity of ischemia (lack of blood flow) to the distal extremities that occurs in Buerger’s, the disease does not involve other organs, unlike many other forms of vasculitis. Even as ulcers and gangrene develop in the digits, organs such as the lung, kidneys, brain, and gastrointestinal (GI) tract remain unaffected. The reasons for the confinement to the extremities and sparing of other organs are not known.
What Causes Buerger’s Disease?
The association of Buerger’s Disease with tobacco use, particularly cigarette smoking, cannot be overemphasized. Most patients with Buerger’s are heavy smokers, but some cases occur in patients who smoke “moderately”; others have been reported in users of smokeless tobacco. It has been postulated that Buerger’s Disease is an “autoimmune” reaction (one in which the body’s immune system attacks the body’s own tissues) triggered by some constituent of tobacco.
Pictured below, are a patient’s fingertips that have developed gangrene. This is a very painful condition which sometimes requires amputation of the affected area.
How is Buerger’s diagnosed?
Buerger’s disease can be mimicked by a wide variety of other diseases that cause diminished blood flow to the extremities. These other disorders must be ruled out with an aggressive evaluation, because their treatments differ substantially from that of Buerger’s Disease (for Buerger’s, there is only one treatment known to be effective: complete smoking cessation — see below).
Diseases with which Buerger’s Disease may be confused include atherosclerosis (build–up of cholesterol plaques in the arteries), endocarditis (an infection of the lining of the heart), other types of vasculitis, severe Raynaud’s phenomenon associated with connective tissue disorders (e.g., lupus or scleroderma), clotting disorders of the blood, and others.
It should be noted that other substances, such as marijuana, have also been associated with a vasculitis similar to Buerger’s or polyarteritis nodosa that should be considered in the differential diagnosis.
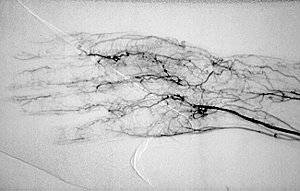
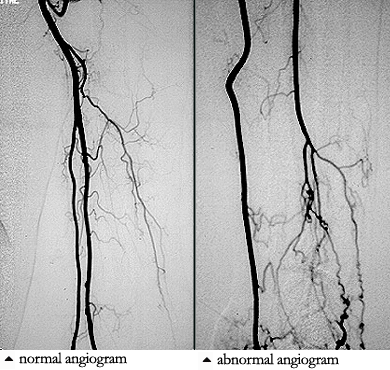
Angiograms of the upper and lower extremities can be helpful in making the diagnosis of Buerger’s disease. In the proper clinical setting, certain angiographic findings are diagnostic of Buerger’s. These findings include a “corkscrew” appearance of arteries that result from vascular damage, particularly the arteries in the region of the wrists and ankles. Angiograms may also show occlusions (blockages) or stenoses (narrowings) in multiple areas of both the arms and legs.
Pictured below on the left is a normal angiogram. On the right, is an abnormal angiogram of an arm demonstrating the classic “corkscrew” appearance of arteries to the hand. The changes are particularly apparent in the blood vessels in the lower right hand portion of the picture (the ulnar artery distribution).
In order to rule out other forms of vasculitis (by excluding involvement of vascular regions atypical for Buerger’s), it is sometimes necessary to perform angiograms of other body regions (e.g., a mesenteric angiogram).
Skin biopsies of affected extremities are rarely performed because of the frequent concern that a biopsy site near an area poorly perfused with blood will not heal well.
Treatment and Course of Buerger’s
It is essential that patients with Buerger’s disease stop smoking immediately and completely. This is the only treatment known to be effective in Buerger’s disease. Patients who continue to smoke are generally the ones who require amputation of fingers and toes.
Despite the clear presence of inflammation in this disorder, anti-inflammatory agents such as steroids have not been shown to be beneficial. Similarly, strategies of anticoagulation (thinning of the blood with aspirin or other agents to prevent clots) have not proven effective. The only way to prevent the progression of the disease is to abstain from all tobacco products.