There are approximately 20 different disorders that are classified as “vasculitis”. “Angiitis” and “Arteritis” are both synonyms for vasculitis, literally meaning “inflammation within blood vessels” or “inflammation in arteries.” Because there are so many types of vasculitis, the group is sometimes referred to in the plural: vasculitides (pronounced “vas que lit’ i deez”).
There are many different types of diseases that belong to this category. Although the diseases are similar in some ways, they often differ with respect to which organs are affected, which medications are used to treat them, and other characteristics.
In general, vasculitis can be grouped based on the size of the blood vessels that are
mainly affected. However, it is important to keep in mind that any sized blood vessels can be
involved.
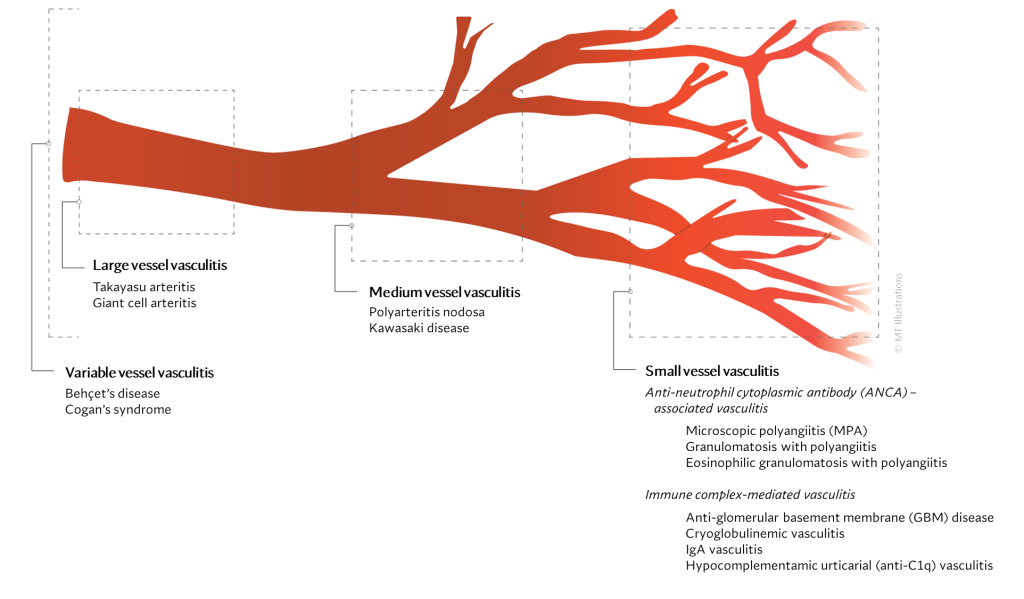
Large vessel vasculitis (LVV)
LVV is characterized by inflammation of the largest-sized blood vessels of the body such
as the aorta, major arteries that deliver blood to distant parts of the body. They also include
large veins that deliver blood back to the heart. These are:
Medium vessel vasculitis (MVV)
MVV is inflammation of the medium-sized blood vessels including arterioles and smaller
veins.
- Polyarteritis nodosa
- Kawasaki disease
Small vessel vasculitis (SVV)
SVV affects the smallest blood vessels of the body called capillaries and venules. SVV
involves inflammation mediated by autoantibodies (antibodies are molecules that usually coats
bacteria and viruses; however, in autoimmune disease, they bind to cells and proteins normally
found in the body, hence the name, autoantibodies). These antibodies can deposit in small vessels
causing restriction of blood flow to tissue.
They can be of two types:
(1) Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV)
- Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA)
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA)
- Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA)
(2) Immune complex small vessel vasculitis
- Anti-glomerular basement membrane
- Cryoglobulinemic vasculitis
- IgA vasculitis
- Hypocomplementamic urticarial vasculitis (anti-C1q vasculitis)
Variable vessel vasculitis (VVV)
This type of vasculitis can involve inflammation of blood vessels of any size.
- BehÇet’s disease
- Cogan’s syndrome
Others:
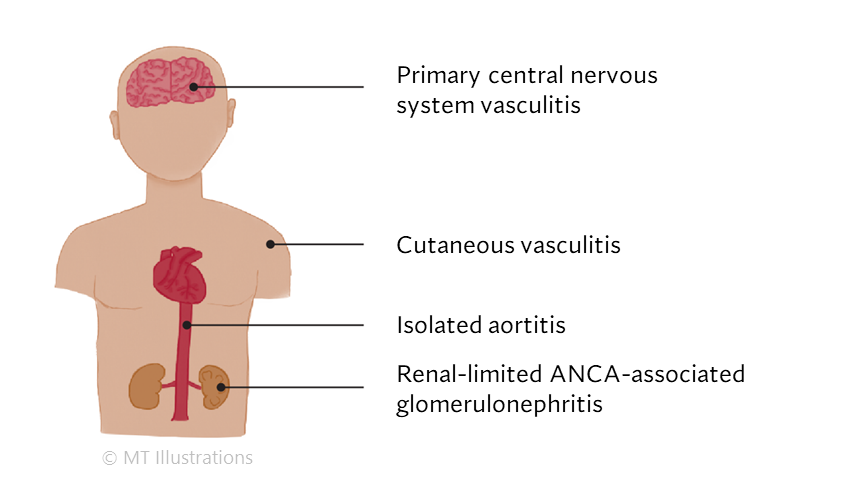
SOV is inflammation affecting the blood vessels that feed a single organ, such as the brain or skin.
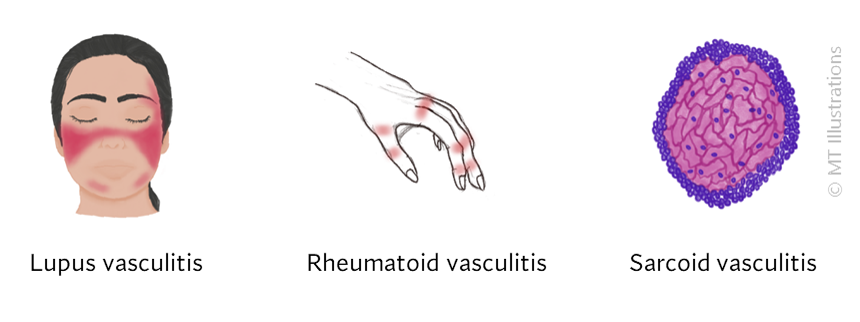
Vasculitis can occur in conjunction with other autoimmune diseases, such as lupus or sarcoidosis.
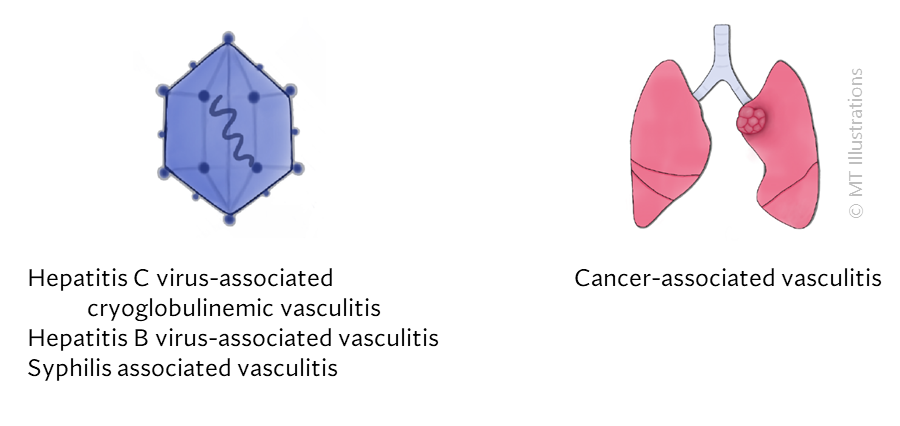
Other diseases, such as infections and cancer, can cause systemic vasculitis as well.
Certain drugs, such as hydralazine and cocaine, can cause vasculitis.



